With Google and other search engines constantly tweaking their ranking algorithms to improve their search results, search engine optimization isn’t something you can do once and forget about. As best practices change, you may need to make adjustments to your website to keep your rankings where you want them to be.
That’s why it’s recommended to conduct an SEO audit every six months, (or after you’ve made any major changes to your site) checking for any penalties, evaluating on- and off-page SEO as well as technical aspects so you can identify problems and address them. just like your car, your website needs a service every now and then to keep it performing the way you want! In other words,it is better to start out fresh and right from the beginning as there are also many HTML editors and Google sites that will teach you how to build a website from scratch and for free.

Here we take a look at the basic steps in conducting your own SEO audit, and what is best left to the professionals.
Google your brand
Just by searching for your own brand name in Google, you’ll already see a few indicators as to the state of your site’s SEO ‘health’. The first result that comes up should be your homepage, and you should see a number of sitelinks listed below the homepage entry. Let’s use Nando’s as an example:
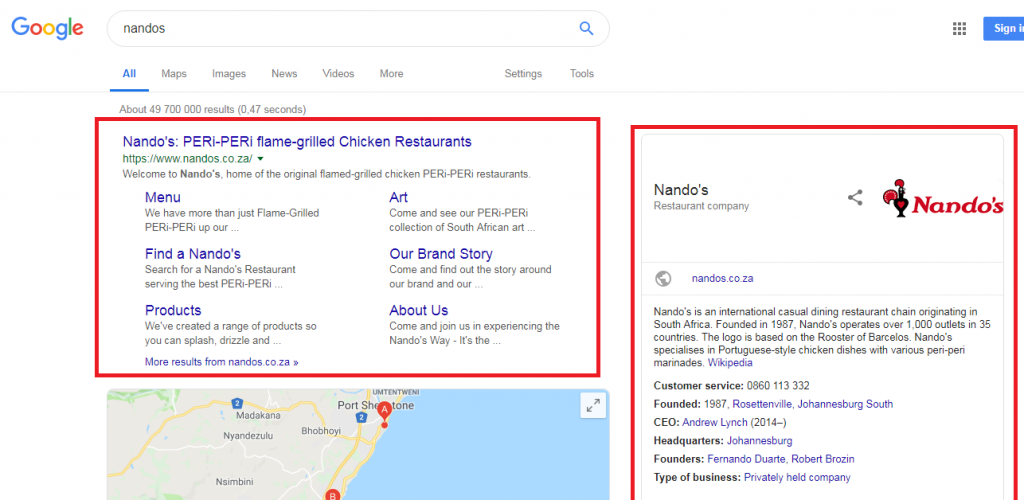
On the right-hand panel, you should see your company’s Google My Business listing appear in the little info block. Check that all these details are correct, and that the headings and descriptions listed under the sitelinks section are accurate.
If you don’t see something similar to this, then there is an issue with your site structure and the SEO on your homepage. You’ll want to correct this before moving onto anything else, and make sure you have an up to date Google My Business listing so visitors know they’re dealing with the right company and can leave reviews and interact with you.
Perform a crawl to find major errors
Search engines use crawlers or spiders to index websites, assessing one page at a time and indexing them accordingly. How often Google crawls your site depends on how frequently you add new content, so avoid adding heaps of content all in one go and then not adding any new content for months on end.
Performing a manual crawl during an SEO audit can give you invaluable insights into issues like broken links, duplicate pages, bad keywords, page title issues, poor images, and excess redirects. Depending on how large your site is, a full crawl can take some time, so start this process early on in your SEO audit.
A few useful tools for performing a crawl include:
Once the report is complete, you can treat it as your SEO ‘to do’ list and start addressing technical issues that could be harming your ranking without you even being aware of them. If you aren’t sure how to fix the errors you find in the report, it’s a good idea to get an SEO services expert on board at this point.
Get rid of ‘zombie’ pages:
Zombie pages are URLs on your website that have been indexed by Google but contain no useful information. These might be navigation links, a page you thought would be necessary but then forgot to add content to, archived pages, thin content pages (less than 50 words) or simply pages that have been added by mistake. If you have lots of these pages indexed by Google, they’re going to hurt your rankings – all without you even knowing they’re there. A good way to ascertain whether you have zombies in your midst is by running a search for:
At the top of the page, you’ll see how many pages Google has indexed for your site:
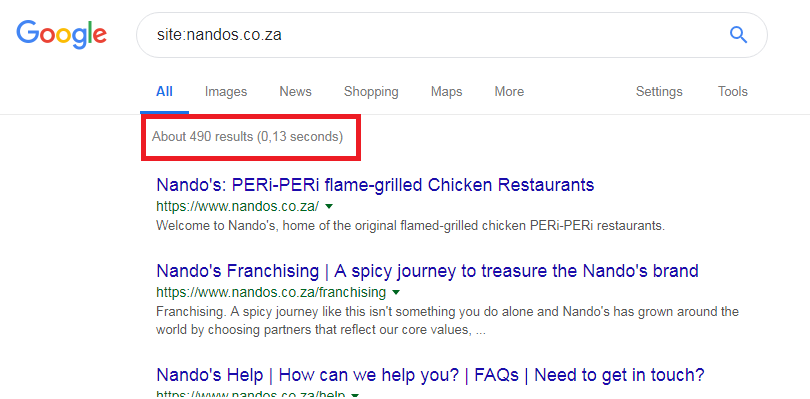
If that number is higher than you expect, then you have a zombie invasion on your hands. Because these pages add no value for visitors, they drag the ranking for your whole site down with them. Getting rid of them (or expanding on the content they contain to make them actually useful) often results in an almost immediate improvement in your page rankings – especially if you have a lot of them – and also makes the rest of your job easier, as you’ll have fewer pages to check during the rest of your SEO audit.
Check your website is mobile friendly
60% of Google searches now start on a mobile device. Because of this, Google announced the rolling out of mobile-first indexing in March 2018. Essentially, this means that Google now uses the mobile version of your website for both mobile and desktop searches. In short, the mobile version of your website will affect your rankings more than the desktop version. To test your site is mobile friendly and get suggestions on improving it, enter your URL into Google’s free Mobile-Friendly Test search.
All the above tools give you a basic starting point to check the SEO health of your website and get a better idea of what needs fixing. You can find more details on performing a full-scale technical SEO audit here and here. If you’re not confident that you know how to fix an issue yourself, it’s better to call in a pro than potentially making matters worse.